Material Defects in Tubing and Welds
Introduction
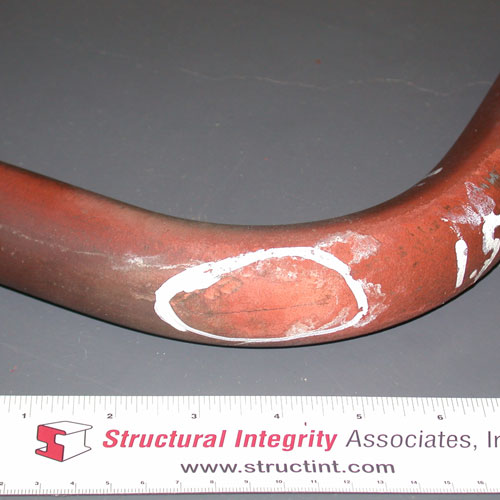
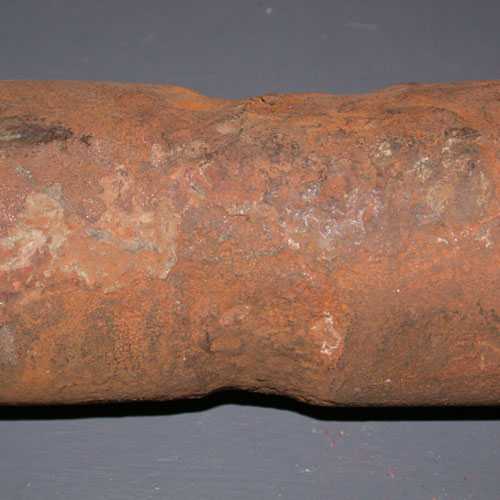
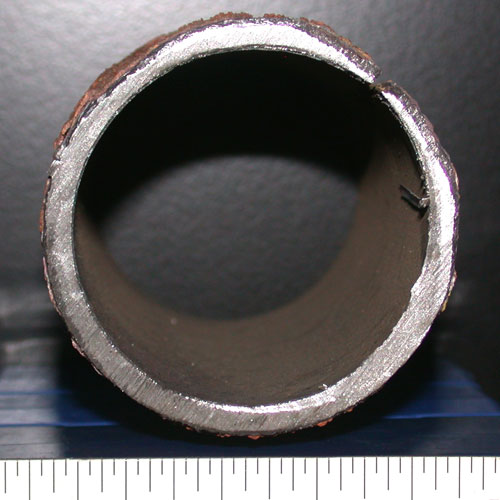
Boiler tubes can fail for reasons other than damage induced during service. In particular, if during the manufacture of a tube or the fabrication of a weld, defects are created that are of a sufficient size and of a sufficiently unfavorable orientation, then the tube or weld may leak or rupture in service.
Description
Mechanism
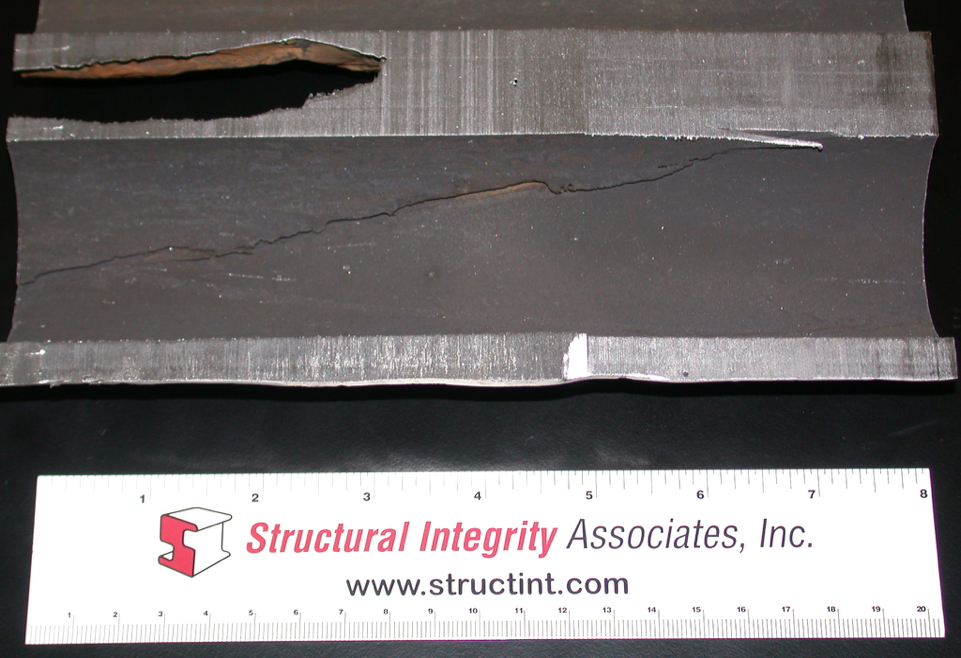
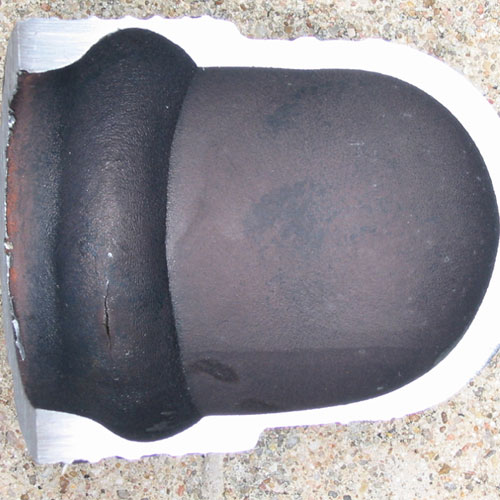
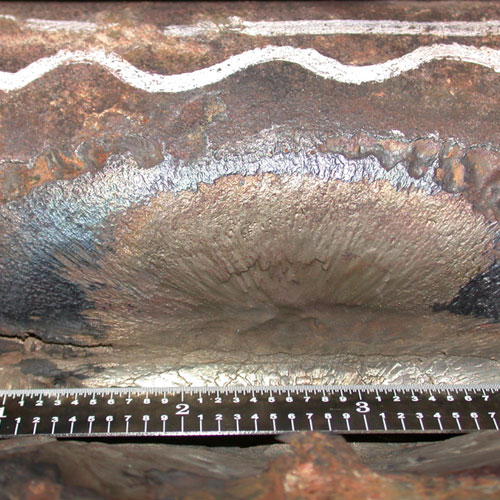
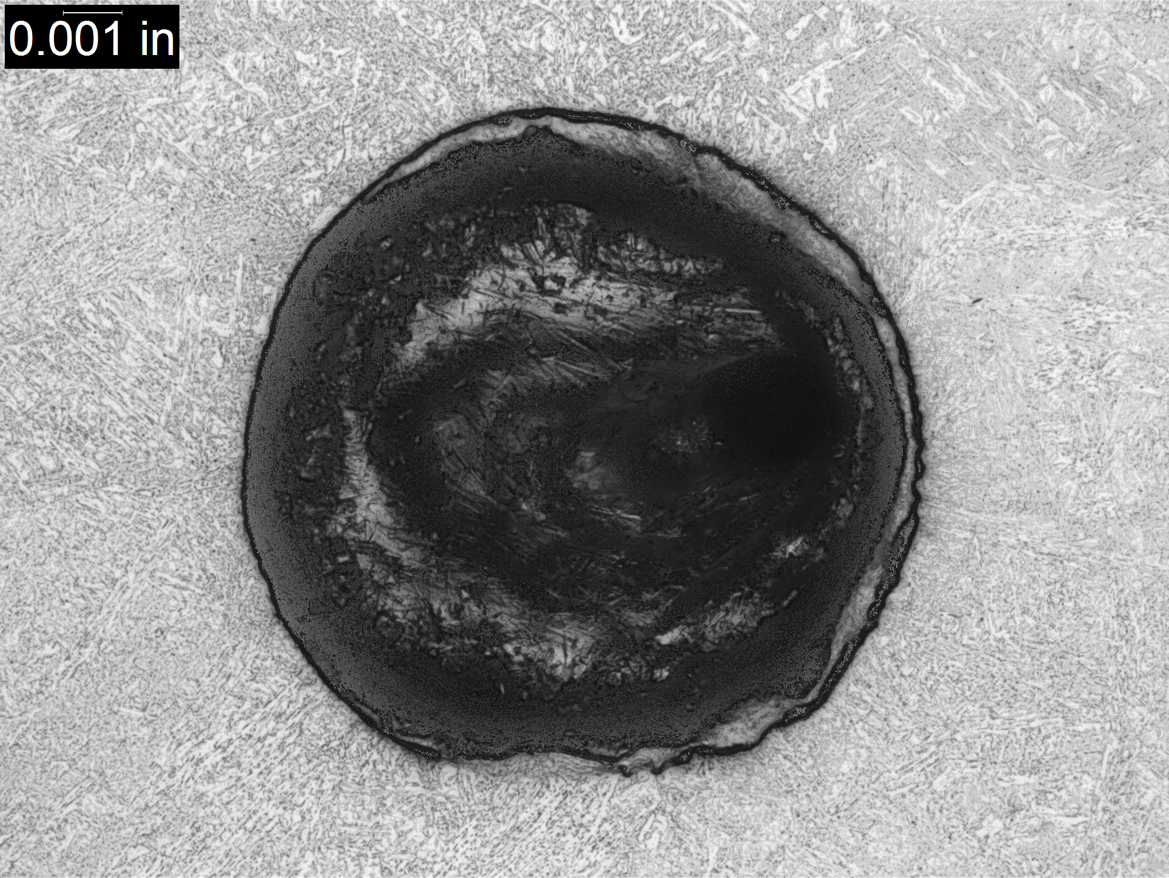
In tubing, defects can include structural discontinuities introduced during the forming and shaping of the tubes, such as laps, seams, deep tool marks, and gouges, as well as processing-related errors, including incorrectly marked material, incorrect heat treatment, and material or debris left inside the tubing following completion of the manufacturing process. For welds the defects can include such conditions as lack-of-fusion, incomplete penetration, severe porosity, entrapped slag, “cold” cracking, “hot” cracking, crater cracking, arc strikes, and burn-through.
Typical Locations
Defects in tubing or welds are, by definition, unplanned and unintentional and, as a result, there are no “typical” locations for failures caused by such defects. Sometimes it is possible to isolate particular heats of tubing that are more likely to contain defects; however, if traceability is not maintained throughout the fabrication and installation phases, this information may be of limited value. The link between a defective weld and either a particular welder or a location with difficult access can in some cases be helpful in identifying other defective welds.
Features
Root Causes
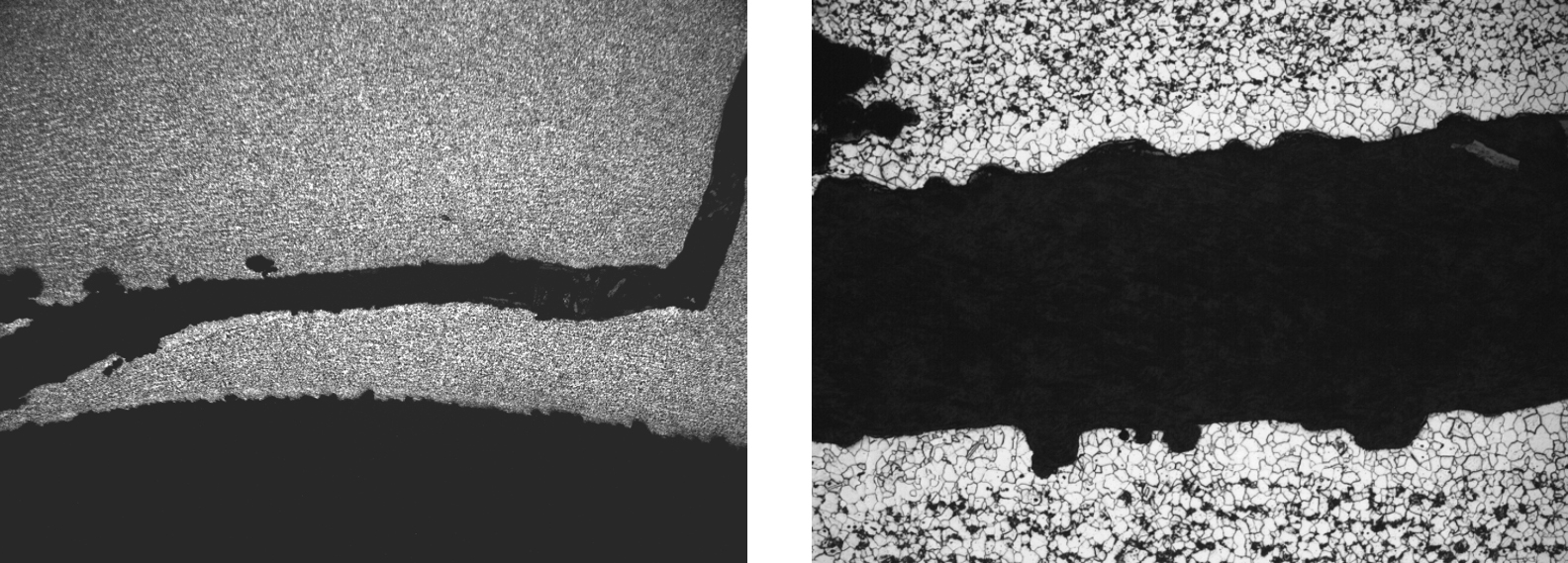
There are a broad range of conditions that can lead to the creation of defects in tubes or welds. In most cases there are distinctive features associated with each of the defective conditions. These features can sometimes be identified by visual examination, and they usually can be confirmed by destructive metallurgical analysis. For example, the presence of a thin decarburized zone surrounding a linear discontinuity extending from the ID surface into the body of a tube is an infallible indicator that the discontinuity is a manufacturing defect that occurred prior to the final high temperature heat treatment. Similarly, the presence of refractory-type material in an elongated discontinuity running along a weld fusion boundary is an indicator of entrapped slag left in the weld, likely due to poor welding technique.
Corrective Actions
Once the nature of the defect has been established, it can be determined whether an inspection program to detect other defective tubes or welds is warranted. In many cases, the defect will be random in its occurrence (e.g., laps in tubing) so that only 100% inspection of all tubing or welds in a particular component, heat, or lot will provide assurance of the elimination of additional failures. Whether such an extensive inspection program is feasible can be determined only through discussions with the client. In other cases, there may be some pattern to the occurrence of the defects (e.g., crater cracking) that would limit the area requiring inspection and make inspection more practical. Any inspection technique used should be matched to the nature of the defect to ensure that the detection and sizing capability are optimized.
As indicated above, the appropriate repair/replacement action will depend on the nature of the defect. In some cases, for example tube laps, only one or two defects among a large population will be large enough to require repair or replacement. In other cases, for example excessive weld push-through on small diameter tubing, all defects in a group of tubes or welds could be potentially significant and require repair or replacement.
SI Services
- Defect identification through destructive metallurgical analysis
- Assistance with determination of the appropriate corrective action based on the nature of the defective condition(s)
- Non-destructive inspection of tubing or welds to detect other defects
- Assistance with repair/replacement actions
Additional information
| Boiler Type | |
|---|---|
| Fuel | |
| Boiler Region | |
| Metallurgy | |
| Failure |